IL2RA(CD25):CD4+CD25+Tregs亚群最特异性标志物,抑制效应T细胞,免疫领域热点分子!
日期:2023-08-17 13:27:28
2023年8月8日,信达生物在Nature Cancer期刊发表了题为“IL-2Rα-biased agonist enhances antitumor immunity by invigorating tumor-infiltrating CD25+CD8+ T cells”文章 [1]。该报道揭示了抗PD-1/IL-2双特异性抗体融合蛋白(IBI363)的早期临床前核心机制研究结果。数年来,随着对T细胞亚群的不断研究,一群能够主动维持免疫平衡和外周免疫耐受的细胞被发现,定义为调节性细胞(Tregs)。T细胞具有异质性,包括CD4+CD25+Tregs,CD8+CD25+Tregs,CD8+CD28+Tregs细胞等,其中CD4+CD25+Tregs是目前研究最多的亚群之一。
IL2通过IL2受体αβγ三聚体诱导激活CD4+CD25+Tregs。CD4+CD25+Tregs细胞是一种负向免疫调控细胞,在抑制自身免疫性疾病的进展、控制潜在有害的炎性反应及维持自身免疫稳态等方面起了关键性的作用。通过调节CD4+CD25+Tregs细胞数量,影响效应T细胞功能,可治疗多种免疫疾病或肿瘤。目前,IL2RA(CD25)作为该亚群的最特异性标志,成为免疫调节研究领域的热点分子!
1. 什么是CD4+CD25+调节性T细胞?
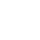
CD4+CD25+调节性T细胞(CD4+CD25+Tregs))是一类特定亚群的CD4+T细胞。它们特征性的表达CD25分子,即IL-2受体α链(IL-2RA),属于职业抑制性T细胞。1995年,Sakaguchi等人首次报道在正常人和小鼠外周血及脾脏组织的CD4+T淋巴细胞中,有一细胞亚群持续高表达CD25分子,进而首次分离出CD4+CD25+T细胞。目前该亚群特异性的标志分子还包括FOXP3,其次CTLA-4、GXTR等,这些标志有助于将CD4+CD25+Tregs从活性T细胞、效应性T细胞和记忆性T细胞中区分出来。CD4+CD25+Tregs具有两大核心功能特性:一是免疫无能性,即不响应IL-2等刺激;二是免疫抑制性,可以抑制效应T细胞增殖,并影响其细胞因子产生(图1) [2-6]。
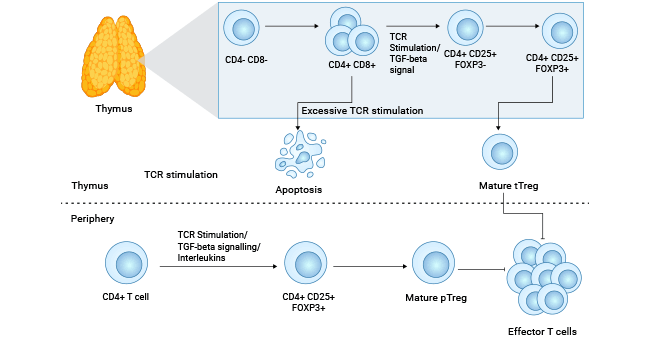
图1. CD25参与Tregs调节性T细胞的发育和免疫调节 [2]
2. 什么是IL2Rα/IL2RA(CD25)?
IL2Rα/IL2RA(又称为CD25)是白细胞介素2(IL-2)受体的α链,其胞浆区域较短,属于一种低亲和性的白介素-2(IL-2)受体。IL-2RA因为可以持续、高水平的表达在静止以及活化的调节性T细胞上,所以是目前最常用的调节性T细胞标记分子。IL-2Rβ(CD122)和IL-2Rγ(CD132)的二聚体形式是IL-2信号通路的必须结构,但仅有IL-2Rβ和IL-2Rγ的二聚体形式存在时,IL-2无法有效的通过IL-2受体复合物信号通路调节T细胞增生。因此,IL-2Rα可以与IL-2受体的β链(CD122)和γ链(CD132)形成复合物,从而增强IL-2与受体的亲和力(图2) [7-11]。
IL2RA(CD25)主要表达于CD4+细胞膜表面,参与调节性CD4+T细胞在IL-2的生理低水平下进行分化和增殖。近些年,CD4+CD25+Tregs细胞亚型,因其具有独特的作用方式和功能特征引起了国内外研究者的共同关注。在CD4+CD25+Tregs细胞中,CD25作为IL-2受体的关键组成部分,使Treg细胞能够响应IL-2信号,发挥免疫调控功能。Treg细胞通过抗原非特异性机制来抑制效应T细胞的激活。总之,IL-2RA(CD25)作为Treg细胞的重要标志,不仅标识了这个特定的细胞亚群,还使CD4+CD25+Tregs能够发挥关键的免疫调控功能 [7-11]。
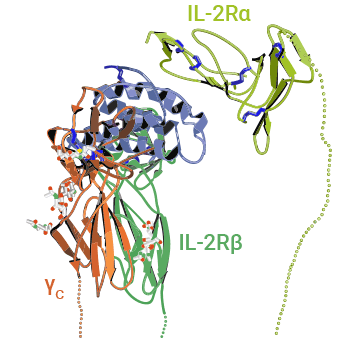
图2. IL-2与IL-2α、β和γ链受体复合物结构示意图 [11]
3. IL2RA相关的调控机制
3.1 IL2/IL2Rα信号通路机制
IL2Rα作为IL-2异源三聚体受体复合物的α链,与IL-2受体β链、γ链形成IL-2受体复合物。IL-2受体复合物本身不具有激活信号通路能力,是通过与非受体型蛋白酪氨酸激酶偶联,激活下游信号传导通路。主要通过以下三条信号通路传导 (图3)[12-14]:
i) Jak-STAT途径。激酶被激活,IL-2R胞内段Jak蛋白结合部分发生磷酸化,启动STAT因子转入细胞核中,使靶基因发挥调控细胞增殖与凋亡的作用。
ii) MAP激酶途径。激酶和Syk激酶活化后,使IL-2R胞内段发生磷酸化,引发Shc蛋白和Grb-2蛋白级联激活,使具有丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶活性的Raf-1蛋白启动MAP激酶途径;另外,在Jak激酶活化后还可以激动Pyk2激酶,从而启动MAP激酶途径;最终调节细胞周期蛋白依赖激酶对特定底物发挥作用,促进细胞增殖。
iii) 磷酸酰肌醇-3-激酶PI3K途径。该过程需要Jak激酶、Pyk2激酶的参与,lck激酶作为启动因子,磷酸酰肌醇-3-激酶与Shc蛋白结合后刺激致癌基因Akt和p70S6k表达,参与调控细胞凋亡及增殖活动。
图3. IL-2/IL-2Rα信号通路机制 [12]
3.2 CD4+CD25+Tregs的免疫负调节机制
IL2RA(CD25)作为Treg细胞的重要标志,不仅标识了CD4+CD25+Tregs这个特定的细胞亚群,还使其能够发挥关键的免疫调控功能。CD25分子在CD4+CD25+ Treg上呈高表达状态,能够与效应细胞竞争性结合IL-2,使效应细胞无法得到生长信号而不能增殖。CD4+CD25+Tregs细胞的主要功能特性是免疫无能性和免疫抑制性。免疫无能性是指在抗原刺激下,Treg呈现无反应状态,即使在高浓度IL-2单独刺激下也呈无应答状态。免疫抑制性是指在T细胞受体(TCR)介导的信号刺激下,调节性T细胞可活化、增殖成为有抑制作用的T淋巴细胞 [13-14]。
近年来体内外研究表明,除了IL-2RA(CD25),细胞因子(IL-10、TGF-β、IL-2、IL-6)和某些细胞膜分子(CTLA-4、GITR)也在CD4+CD25+Tregs功能的发挥中起了一定的作用 (图4)[15-18]。目前对CD4+CD25+Tregs的效应机制还不十分明确。最初的体外研究明确支持CD4+CD25+Tregs是通过与其他细胞直接接触发挥抑制作用这一观点。因此,细胞-细胞互相接触是该亚型发挥作用的先决条件。
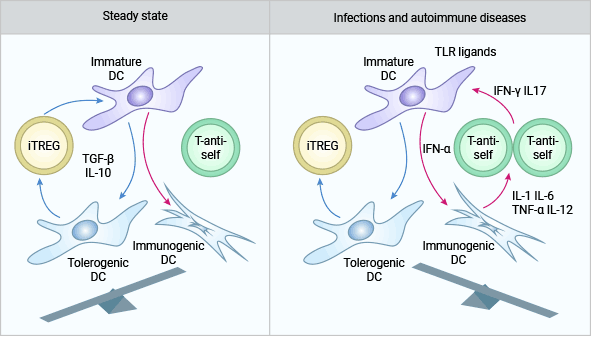
图4. IL-10和TGF-β参与CD4+CD25+Treg(iTREG)的免疫调节作用机制 [16]
4. CD4+CD25+Tregs在多种疾病中的作用
IL2RA,即DC25,主要表达于CD4+CD25+Tregs细胞表面。CD4+CD25+Tregs作为新近发现的,一个具有独特免疫调节作用的T细胞亚群,其在维持机体免疫耐受和调节免疫反应中起着重要作用!随着研究的深入,该亚型逐渐成为最近几年来研究的热点。
4.1 CD4+CD25+Tregs与自身免疫性疾病
目前已有大量的证据表明CD4+CD25+Tregs细胞数量和或功能异常是打破自身免疫耐受与诱发许多自身免疫性疾病的重要因素。与正常人相比I型糖尿病患者的外周血中CD4+CD25+Tregs细胞数量均明显降低,并且与疾病的严重程度有关。除了数量缺少外,I型糖尿病患者的CD4+CD25+Tregs细胞的免疫抑制功能也降低。在某些情况下,这些T细胞虽然数量没有明显变化,但对抑制T细胞增殖的作用减少,同时分泌IFN-γ增加、分泌IL-10减少。这可能导致CD4+CD25+T细胞的抑制功能减弱,影响对胰岛的保护 [19-20]。
在系统性红斑狼疮SLE中,研究发现患者外周血CD4+CD25high T细胞与CD4+CD25int T细胞的比率降低,说明SLE存在免疫失衡,主要表现为抑制功能细胞下降,而效应性T细胞升高。通过增加CD4+CD25high T细胞的数量和功能或抑制效应T细胞可作为SLE治疗靶点 [21]。在另外一些自身免疫性疾病中,如多发性硬化病 [22]、类风湿关节炎 [23]、银屑病 [24]、Wegner’s肉芽肿病 [25]和重症肌无力 [26]等,虽然CD4+CD25+Tregs细胞的数量正常,但其免疫抑制活性是下降的或者缺乏的。
4.2 CD4+CD25+Tregs与移植物抗宿主病
CD4+CD25+Tregs在移植物抗宿主病(GVHD)中发挥重要作用。GVHD是一种免疫性疾病,常见于异种基因造血干细胞移植。研究表明,CD4+CD25+Tregs可以调节GVHD的发生。供者淋巴细胞中去除CD4+CD25+T细胞或受体中去除CD25+T细胞会增加GVHD的风险,而输注新鲜的供体CD4+CD25+T细胞可以减轻GVHD。其中,CD4+CD25+CD62L+Treg对急性GVHD的调节作用显著。不同的CD4+CD25+Tregs亚群在抑制GVHD中的作用有所不同。这些发现对于GVHD的临床预防和治疗提供了有益的信息 [27-28]。
4.3 CD4+CD25+Tregs与肿瘤
许多肿瘤抗原为自身抗原,CD4+CD25+Tregs能抑制T细胞对外来和自体抗原的免疫应答,因而在维持对自身成分耐受的同时,也会阻止机体对肿瘤细胞的免疫应答,从而导致了肿瘤的免疫逃逸 [29-30]。在急性髓系白血病(acute myeloid leukemia,AML)中,CD25+AML患者的白血病细胞高表达髓系抗原CD11b、CD36;淋系抗原CD4、CD22;骨髓干细胞抗原CD123。而低表达浆细胞抗原CD38及NK细胞抗原CD56 [31-32];在卵巢癌中,肿瘤细胞分泌CCL22,招募CD4+CD25+Tregs至肿瘤部位,导致CD4+CD25+Tregs在癌肿组织中聚集,而在正常的卵巢组织中几乎不能看到CD4+CD25+Tregs。对于肿瘤而言,去除这群细胞可能有助于诱发有效的肿瘤免疫 [33-34]。
4.4 CD4+CD25+Tregs与其它疾病
CD4+CD25+Tregs的抑制作用使得幽门螺杆菌无法被免疫系统清除而长期存在,对胃、十二指肠造成了损害,导致胃、十二指肠溃疡甚至癌变 [35];IL2RA基因的rs3118470位点的基因多态性与斑秀的家族史以及病情严重程度存在着一定的相关性 [36];在妊娠小鼠的脾脏、回肠淋巴结以及外周血中,CD4+CD25+Tregs的比例明显高于非妊娠对照组小鼠。如果将抗CD25单抗克隆体输注给小鼠,则会导致其流产。说明CD4+CD25+Tregs在诱导母胎免疫耐受方面起着重要作用 [37]。
在大鼠脑缺血再灌注CD4+CD25+Tregs细胞输注移植治疗模型中,CD4+CD25+Tregs细胞可以减小大脑中动脉阻塞缺血再灌注(MCAO/R)大鼠脑梗死体积,降低缺血后神经功能缺损,提高神经功能恢复。此外,CD4+CD25+Tregs细胞还可降低缺血对寡突胶质细胞和轴突造成的损害,减轻脑缺血后白质损伤 [38]。
5. IL2RA的临床研究前景
目前,有多家机构在研究靶向IL-2RA(CD25)的药物,包括三生国健药业(上海)股份有限公司、信达生物、Ligand Pharmaceuticals, Inc.、Eisai Co., Ltd.和Novartis Pharma AG等。三种靶向CD25/IL-2RA的药物已经获得批准上市,分别是Daclizumab达克珠单抗和Basiliximab巴利昔单抗(均用于肾移植排斥反应)、Denileukin Diftitox地尼白介素2(用于外周T细胞淋巴瘤和转移性黑色素瘤)。此外,还有一些药物正在进行临床试验,如Inolimomab伊诺莫单抗已处于批准上市阶段,用于移植物抗宿主病GVHD。CD4+CD25+Tregs作为一个具有免疫调节作用的T淋巴细胞亚群,对它的研究正步入到一个新阶段!因此,对Treg细胞最特异性标志IL-2RA(CD25)作用的深入研究将有助于对机体免疫调节机制的了解,最终为相关疾病的治疗开辟新的免疫治疗途径。
为鼎力协助科研和药企人员针对IL-2RA(CD25)在多种免疫疾病和肿瘤中的临床应用研究,CUSABIO推出IL-2RA(CD25)活性蛋白(Code: CSB-MP011649HU3),助力您在IL-2RA(CD25)机制方面的研究或其潜在临床价值的探索。
IL-2RA(CD25)蛋白
by SDS-PAGE
Purity was greater than 95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.(Tris-Glycine gel) Discontinuous SDS-PAGE (reduced) with 5% enrichment gel and 15% separation gel.
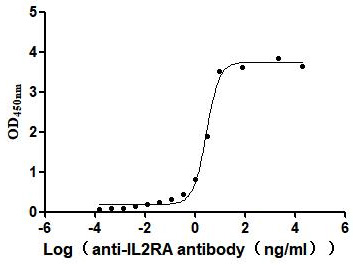
Immobilized Human IL2RA at 2μg/mL can bind Anti-IL2RA recombinant antibody (CSB-RA011649MA1HU),the EC50 is 2.463-3.353 ng/mL.
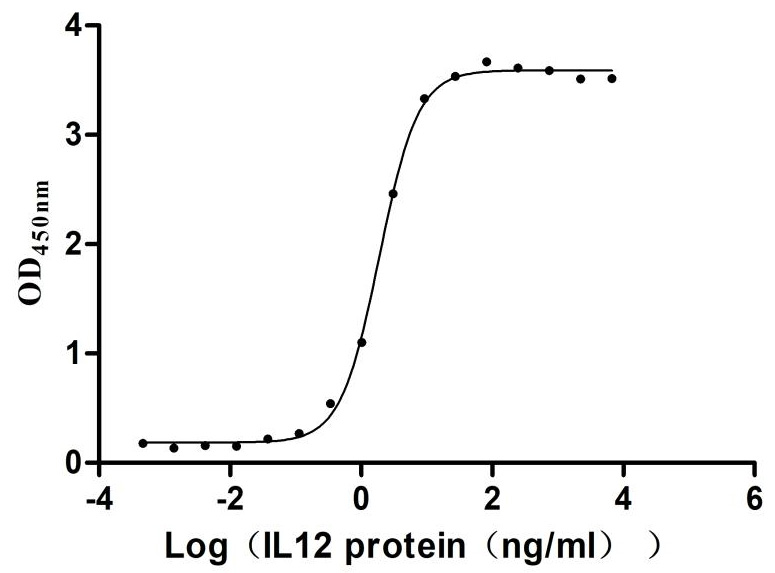
Immobilized Human IL2RA at 2μg/mL can bind Human IL2 (CSB-MP011629HU),the EC50 is 1.693-2.039 ng/mL.
参考文献:
[1] Wu, W., Chia, T., Lu, J. et al. IL-2Rα-biased agonist enhances antitumor immunity by invigorating tumor-infiltrating CD25+CD8+ T cells. Nat Cancer ( 2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43018-023-00612-0
[2] Dhawan, Manish, et al. "Regulatory T Cells (Tregs) and COVID-19: Unveiling the Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Potentialities with a Special Focus on Long COVID." Vaccines 11.3 (2023): 699.
[3] Sakaguchi, Shimon, et al. "Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune diseases." Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md.: 1950) 155.3 (1995): 1151-1164. 1151-1164.
[4] Maes, Michael. T cell activation via the CD40 ligand and transferrin receptor and deficits in T regulatory cells are associated with major depressive disorder and severity of depression. T cell activation via the CD40 ligand and transferrin receptor and deficits in T regulatory cells are associated with major depressive disorder and severity of depression.
[5] Walker, Lucy SK. "CD4+ CD25+ Treg: divide and rule?." Immunology 111.2 (2004): 129-137.
[6] Wan, Yuling, et al. "Hyperfunction of CD4 CD25 regulatory T cells in de novo acute myeloid leukemia." BMC cancer 20 (2020): 1-10.
[7] de Goër de Herve, Marie-Ghislaine, et al. "CD25 appears non essential for human peripheral Treg maintenance in vivo." PloS one 5.7 (2010): e11784.
[8] Spangler, Jamie B., et al. "Antibodies to interleukin-2 elicit selective T cell subset potentiation through distinct conformational mechanisms." Immunity 42.5 (2015): 815-825.
[9] Hsieh, Elena WY, and Joseph D. Hernandez. "Clean up by aisle 2: roles for IL-2 receptors in host defense and tolerance." Current Opinion in Immunology 72 ( 2021): 298-308.
[10] Ye, Congxiu, David Brand, and Song G. Zheng. "Targeting IL-2: an unexpected effect in treating immunological diseases." Signal transduction and targeted therapy 3.1 (2018): 2.
[11] Wang, Xinquan, Mathias Rickert, and K. Christopher Garcia. "Structure of the Quaternary Complex of Interleukin-2 with Its α, ß, and γc Receptors." Science 310.5751 (2005): 1159-1163.
[12] Amaria, Rodabe N., et al. "Update on use of aldesleukin for treatment of high-risk metastatic melanoma." ImmunoTargets and therapy (2015): 79-89.
[13] Tilley, Jefferson W., et al. "Identification of a small molecule inhibitor of the IL-2/IL-2Rα receptor interaction which binds to IL-2." Journal of the American Chemical Society 119.32 (1997): 7589-7590.
[14] Zhang, Bo, et al. "Proximity-enabled covalent binding of IL-2 to IL-2Rα selectively activates regulatory T cells and suppresses autoimmunity." Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 8.1 (2023): 28.
[15] Shatrova, Alla N., et al. "Time-dependent regulation of IL-2R α-chain (CD25) expression by TCR signal strength and IL-2-induced STAT5 signaling in activated human blood T lymphocytes." PLoS One 11.12 (2016): e0167215.
[16] Horwitz, David A et al. "Natural and TGF-beta-induced Foxp3(+)CD4(+) CD25(+) regulatory T cells are not mirror images of each other. " Trends in immunology vol. 29, 9 (2008): 429-35. doi:10.1016/j.it.2008.06.005
[17] Nasiri, Mahboobeh, and Zarnegar Rasti. "CTLA-4 and IL-6 gene polymorphisms: risk factors for recurrent pregnancy loss." human immunology 77.12 (2016). : 1271-1274.
[18] Ware, Michael Brandon, et al. "Dual IL-6 and CTLA-4 blockade regresses pancreatic tumors in a T cell-and CXCR3-dependent manner." JCI insight 8.8 (2023).
[19] Peng, Yujia, et al. "CD25: A potential tumor therapeutic target." International Journal of Cancer 152.7 (2023): 1290-1303.
[20] Qureshi, Farhan M., et al. "Immunotherapy With Low-Dose IL-2/CD25 Prevents β-Cell Dysfunction and Dysglycemia in Prediabetic NOD Mice." Diabetes 72.6 (2023): 769-780.
[21] Eissa, Amal H., et al. "Protective role of T regulatory (Treg) cells in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with nephritis." The Egyptian Rheumatologist 45.1 (2023): 61-65.
[22] Pfender, Nikolai, and Roland Martin. "Daclizumab (anti-CD25) in multiple sclerosis." Experimental neurology 262 (2014): 44-51.
[23] Lawson, C. A., et al. "Early rheumatoid arthritis is associated with a deficit in the CD4+ CD25 high regulatory T cell population in peripheral blood." Rheumatology 45.10 (2006): 1210-1217.
[24] Mrowietz, Ulrich, Kejian Zhu, and Enno Christophers. "Treatment of severe psoriasis with anti-CD25 monoclonal antibodies. "Archives of Dermatology 136.5 (2000): 675-676.
[25] Abdulahad, Wayel H., et al. "Functional defect of circulating regulatory CD4+ T cells in patients with Wegener's granulomatosis in remission." Arthritis & Rheumatism 56.6 (2007): 2080-2091.
[26] Zhang, Min, et al. "Expression of immune molecules CD25 and CXCL13 correlated with clinical severity of myasthenia gravis." Journal of Molecular Neuroscience 50 (2013): 317-323.
[27] Chen, Alex, et al. "NEO-TRA1: A CD25-Targeted De Novo non-Alpha Agonist of the IL-2 Receptor Selectively Expands Regulatory T Cells." Blood 140. Supplement 1 (2022): 1652-1653.
[28] Schneider, Jessica, et al. "Healthy-like CD4+ regulatory and CD4+ conventional T-cell receptor repertoires predict protection from GVHD following donor lymphocyte infusion." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23.18 (2022): 10914.
[29] Rech, Andrew J., and Robert H. Vonderheide. "Clinical use of anti-CD25 antibody daclizumab to enhance immune responses to tumor antigen vaccination by targeting regulatory T cells." Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1174.1 (2009): 99-106.
[30] Li, Hui, et al. "CD 4+ CD 25+ Regulatory T Cells Decreased the Antitumor Activity of Cytokine-Induced Killer (CIK) Cells of Lung Cancer Patients." Journal of clinical immunology 27 (2007): 317-326.
[31] Gönen, Mithat, et al. "CD25 expression status improves prognostic risk classification in AML independent of established biomarkers: ECOG phase 3 trial , E1900." Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology 120.11 (2012): 2297-2306.
[32] Nakase, Kazunori, et al. "CD22 expression in acute myeloid leukemia: close correlation with interleukin-2 receptor α-chain (CD25) expression and poor prognosis." Leukemia & Lymphoma 63.9 (2022): 2251-2253.
[33] Woo, Edward Y., et al. "Regulatory CD4+ CD25+ T cells in tumors from patients with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer and late-stage ovarian cancer." Cancer research 61.12 (2001): 4766-4772.
[34] deLeeuw, Ronald J., et al. "CD25 identifies a subset of CD4+ FoxP3- TIL that are exhausted yet prognostically favorable in human ovarian cancer." Cancer immunology research 3.3 (2015): 245-253.
[35] Stuller, Kathleen A., et al. "CD25+ T cells induce Helicobacter pylori-specific CD25- T-cell anergy but are not required to maintain persistent hyporesponsiveness." European journal of immunology 38.12 (2008): 3426-3435.
[36] Miao, Y., et al. "Association analysis of the IL2RA gene with alopecia areata in a Chinese population." Dermatology 227.4 (2014): 299-304.
[37] Dimova, Tanya, et al. "Maternal Foxp3 expressing CD4+ CD25+ and CD4+ CD25- regulatory T-cell populations are enriched in human early normal pregnancy decidua: A phenotypic study of paired decidual and peripheral blood samples." American journal of reproductive immunology 66 (2011): 44-56.
[38] Li, Ting-ting, et al. "Effect and Mechanism of Sodium Butyrate on Neuronal Recovery and Prognosis in Diabetic Stroke." Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology (2023): 1-17.